- Appareil d'essai de dureté Micro Vickers
- Appareil d'essai de dureté Vickers
- Capteur de dureté Vickers
- Appareil d'essai de dureté Rockwell
- Appareil d'essai de dureté Brinell
- Appareil de dureté Leeb
- Appareil de mesure de la dureté Shore
- Testeur de dureté Webster
- Appareil de mesure de la dureté Barcol
- Barre d'essai de dureté
Portable Hardness Tester Power Guide Smart Reasons for Accurate On-Site Testing
Outline for the Article on Portable Hardness Tester
| Domaine thématique | Couverture détaillée avec des mots-clés LSI |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Portable Hardness Tester | portable hardness testing |
| Definition of Portable Hardness Tester | handheld hardness tester |
| Importance of Portable Hardness Testing | on-site material testing |
| Evolution of Portable Hardness Testers | field testing technology |
| Fundamental Principle of Portable Hardness Testing | rebound and ultrasonic methods |
| Key Advantages of Portable Hardness Testers | mobility and efficiency |
| Limitations of Portable Hardness Testers | accuracy considerations |
| Main Types of Portable Hardness Testers | Leeb, UCI, Rockwell portable |
| Leeb Portable Hardness Tester | dynamic rebound method |
| Ultrasonic Portable Hardness Tester | UCI technology |
| Portable Rockwell Hardness Tester | static indentation |
| Digital Portable Hardness Testers | mesure électronique |
| Automatic Portable Hardness Testers | smart operation |
| Materials Suitable for Portable Hardness Testing | métaux et alliages |
| Portable Hardness Testing for Steel | heat treatment inspection |
| Portable Hardness Testing for Aluminum | alloy verification |
| Portable Hardness Testing for Cast Iron | heavy components |
| Portable Hardness Testing for Non-Ferrous Metals | alliages de cuivre |
| Surface Condition Requirements | preparation guidelines |
| Précision et répétabilité | reliability in the field |
| Calibration and Verification | maintaining accuracy |
| Standards for Portable Hardness Testers | ASTM, ISO |
| Applications dans l'industrie manufacturière | production inspection |
| Applications dans le domaine du contrôle de la qualité | essais d'acceptation |
| Applications in Maintenance and Inspection | in-service testing |
| Applications dans l'industrie automobile | vehicle components |
| Applications dans l'industrie aérospatiale | safety-critical parts |
| Applications in Energy and Heavy Industry | pipelines and turbines |
| Data Recording and Reporting | documentation numérique |
| Selecting the Right Portable Hardness Tester | guide d'achat |
| Erreurs de test courantes | conseils de prévention |
| Maintenance of Portable Hardness Testers | long-term use |
| Intégration avec les systèmes numériques | Industrie 4.0 |
| Expertise et solutions en matière de marques | Johoyd portable hardness tester |
| Future Trends in Portable Hardness Testing | smart diagnostics |
| FAQ | questions courantes |
| Conclusion | résumé |

Introduction
A portable hardness tester has transformed the way industries evaluate material strength outside traditional laboratories. Instead of cutting samples or transporting heavy components, engineers can now perform accurate hardness testing directly on-site.
From manufacturing floors to remote inspection sites, portable hardness testers offer flexibility, speed, and reliability. As industries demand faster decisions and reduced downtime, these compact testing tools have become essential for modern quality assurance.
Testeur de dureté portable
A portable hardness tester is a compact device designed to measure material hardness directly on large, heavy, or installed components. It delivers immediate results while maintaining acceptable accuracy for industrial applications.
This makes it ideal for field testing, maintenance, and production environments.
Definition of Portable Hardness Tester
A portable hardness tester is a handheld or lightweight instrument that evaluates hardness using dynamic, ultrasonic, or static indentation principles. Unlike bench machines, it does not require sample removal.
Its design focuses on mobility without sacrificing reliability.
Importance of Portable Hardness Testing
Portable hardness testing is important because it saves time and cost. It eliminates the need to cut samples or halt production.
By enabling in-situ inspection, it supports faster decision-making and reduces operational risk.
Evolution of Portable Hardness Testers
Early portable hardness testers offered limited accuracy and manual readings. Over time, digital sensors, microprocessors, and improved impact devices enhanced performance.
Modern portable hardness testers now rival laboratory systems for many applications.
Fundamental Principle of Portable Hardness Testing
Portable hardness testers operate by measuring resistance to deformation. Depending on the method, this may involve rebound velocity, ultrasonic frequency change, or indentation depth.
The measurement is converted into standardized hardness values.
Key Advantages of Portable Hardness Testers
Portable hardness testers offer several advantages:
- On-site testing capability
- Minimal sample preparation
- Fast results
- Reduced downtime
These benefits make them indispensable in industrial environments.
Limitations of Portable Hardness Testers
Despite their benefits, portable hardness testers have limitations. Surface condition, mass, and geometry can affect accuracy.
Understanding these factors ensures reliable results.
Main Types of Portable Hardness Testers
Portable hardness testers are available in several types, each suited to specific applications.
Common types include Leeb, ultrasonic contact impedance, and portable Rockwell testers.
Leeb Portable Hardness Tester
The Leeb portable hardness tester uses a dynamic rebound method. An impact body strikes the surface, and rebound velocity is measured.
It is widely used for large metal components.
Ultrasonic Portable Hardness Tester
Ultrasonic portable hardness testers use UCI technology. They measure frequency changes caused by indentation under load.
They are ideal for thin parts and surface-hardened materials.
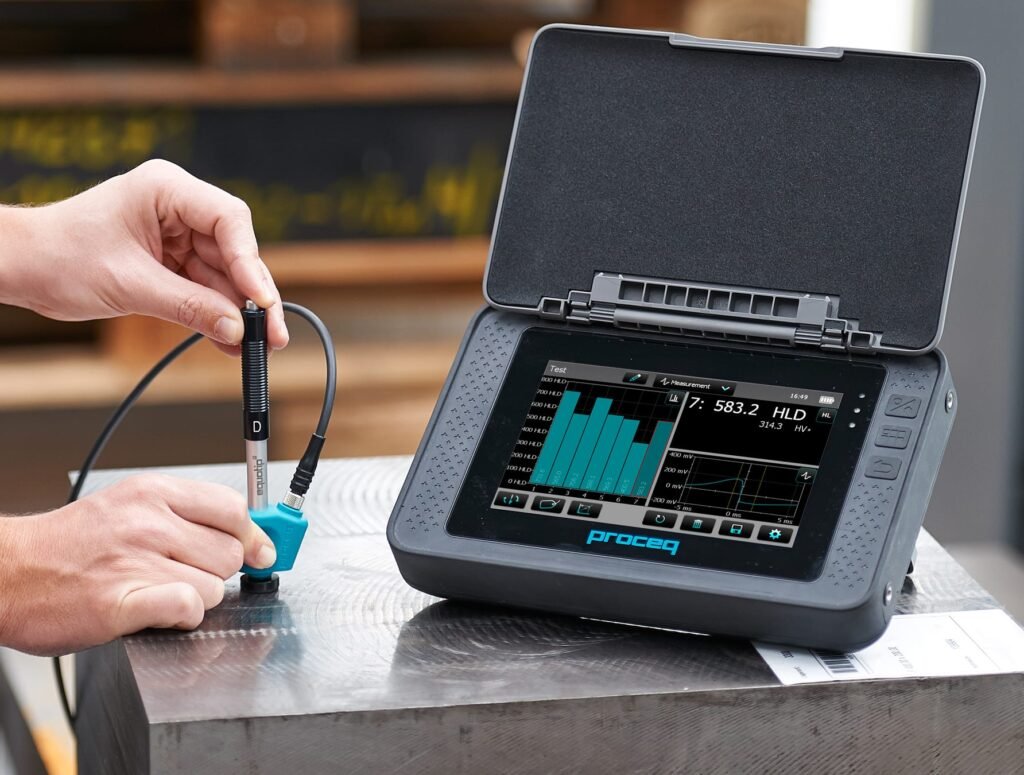

Portable Rockwell Hardness Tester
Portable Rockwell testers apply a static load to measure indentation depth. They provide direct Rockwell values.
These testers are suitable for critical applications.
Digital Portable Hardness Testers
Digital portable hardness testers feature electronic displays and data storage. They reduce operator influence and improve repeatability.
Digital systems support traceable reporting.
Automatic Portable Hardness Testers
Automatic portable testers control loading and measurement automatically. They increase consistency and reduce human error.
Automation improves field efficiency.
Materials Suitable for Portable Hardness Testing
Portable hardness testers are mainly used for metals and alloys. Steel, aluminum, cast iron, and non-ferrous metals are commonly tested.
Correct method selection is essential.
Portable Hardness Testing for Steel
Steel components often require on-site hardness verification. Portable hardness testers confirm heat treatment and strength.
This is critical for safety-related parts.
Portable Hardness Testing for Aluminum
Aluminum alloys need careful testing due to lower hardness. Ultrasonic portable hardness testers are often preferred.
They deliver precise results.
Portable Hardness Testing for Cast Iron
Cast iron components are large and heavy. Leeb portable hardness testers provide representative measurements.
They support heavy industry inspection.
Portable Hardness Testing for Non-Ferrous Metals
Non-ferrous metals require controlled testing. Portable hardness testers help verify material consistency.
They support electrical and thermal applications.
Surface Condition Requirements
Surface condition significantly affects portable hardness testing. Clean, flat surfaces produce reliable results.
Minimal preparation improves efficiency.
Précision et répétabilité
Accuracy depends on calibration, surface condition, and operator technique. Repeatability improves with digital and automatic testers.
Consistent procedures enhance reliability.
Calibration and Verification
Regular calibration ensures accurate measurements. Verification blocks support confidence in field testing.
Calibration is essential for quality systems.
Standards for Portable Hardness Testers
Portable hardness testers follow ASTM and ISO standards. Standardization ensures comparability of results.
Compliance supports audits.
Applications dans l'industrie manufacturière
Manufacturers use portable hardness testers for in-process inspection. They verify consistency without stopping production.
Quick feedback improves control.
Applications dans le domaine du contrôle de la qualité
Quality control teams rely on portable hardness testers for acceptance testing. They support incoming and outgoing inspections.
Reliability is critical.
Applications in Maintenance and Inspection
Maintenance teams use portable hardness testers to assess wear and degradation. Testing supports asset reliability.
On-site inspection reduces downtime.
Applications dans l'industrie automobile
Automotive components require strict hardness control. Portable hardness testers support safety and durability checks.
They enable fast inspection.
Applications dans l'industrie aérospatiale
Aerospace applications demand accurate on-site testing. Portable hardness testers support compliance and traceability.
Precision is essential.
Applications in Energy and Heavy Industry
Pipelines, turbines, and pressure vessels are tested using portable hardness testers. They support safety and compliance.
Field testing is critical.
Data Recording and Reporting
Modern portable hardness testers store data digitally. Reports support documentation and traceability.
Connectivity improves efficiency.
Selecting the Right Portable Hardness Tester
Selection depends on material type, surface condition, and accuracy requirements. Expert guidance ensures optimal performance.
The right choice improves results.
Erreurs de test courantes
Common errors include poor surface preparation and incorrect probe selection. Training reduces mistakes.
Les procédures standardisées améliorent la cohérence.
Maintenance of Portable Hardness Testers
Routine maintenance preserves accuracy. Proper storage and handling extend service life.
Maintenance supports reliability.
Intégration avec les systèmes numériques
Portable hardness testers increasingly integrate with digital quality systems. Data supports smart manufacturing.
Connectivity enhances insight.
Expertise et solutions en matière de marques
Fiable portable hardness tester solutions require precision engineering and professional support. Johoyd, par le biais de https://hardnesstests.com, provides advanced portable hardness testers designed for field inspection, manufacturing, and quality control, delivering accuracy, durability, and compliance for global industries.

Future Trends in Portable Hardness Testing
Future trends include AI-assisted evaluation, wireless data transfer, and enhanced automation. These advancements will further improve field testing efficiency.
Questions fréquemment posées
What is a portable hardness tester used for?
It measures material hardness directly on-site.
Les essais de dureté portables sont-ils précis ?
Yes, when properly calibrated and used correctly.
Quels matériaux peuvent être testés ?
Mainly metals and alloys.
Do portable hardness testers follow standards?
Oui, les normes ASTM et ISO s'appliquent.
Is surface preparation required?
Minimal preparation is usually sufficient.
Can data be stored digitally?
Yes, modern testers support digital storage.
Conclusion
A portable hardness tester is an essential tool for modern industry, enabling fast, reliable, and cost-effective on-site hardness evaluation. By reducing downtime and improving inspection flexibility, it supports quality assurance and operational efficiency.
With trusted brands like Johoyd offering professional solutions through hardnesstests.com, industries can rely on portable hardness testers that combine accuracy, durability, and advanced technology. As innovation continues, portable hardness testing will remain a cornerstone of industrial inspection.
Liens internes suggérés
- Industrial Hardness Testers
- Quality Control Hardness Testing
Liens sortants suggérés
- ASTM Portable Hardness Testing Standards
- Lignes directrices ISO pour la mesure de la dureté


